When you need to create custom models for your projects, the first step is to choose the right modeling method. You’ve probably encountered situations where you started with one modeling method and later realized it had significant limitations. The complexity of the model, the level of detail, animation requirements, rigging needs, and more all influence the choice of modeling technique in each project. For simple objects, polygon modeling might be suitable, while NURBS could be better for other scenarios. Understanding the different methods, their advantages, limitations, and tools is essential for making the right choice. In this article, we’ll delve into NURBS modeling, and in future articles, we’ll explore other common modeling methods.
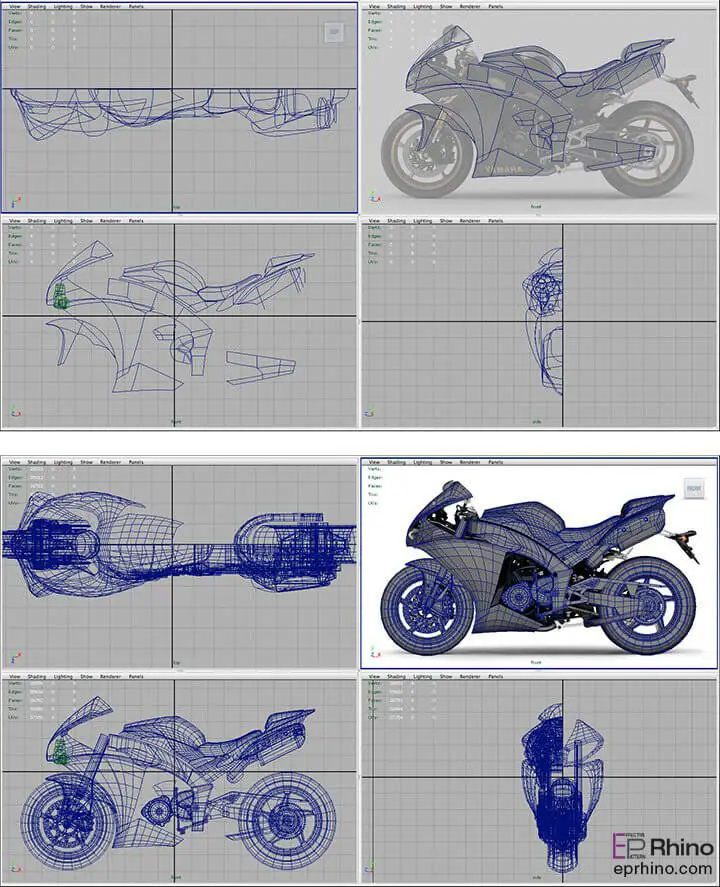
The existence of multiple modeling methods in computer graphics is due to the various mathematical functions that can be used to create 3D surfaces. One of the most important and widely used methods is NURBS, which stands for Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline. It’s important to note that these methods are based on mathematical functions and structures, so they are not exclusive to computer graphics. They have also been used in engineering calculations and manual drafting. With the advent of computers, these calculations were delegated to machines, enabling more accurate and efficient use of these methods. Since the 1990s, NURBS modeling has gained popularity in computer graphics, and software developers have integrated extensive tools for creating and editing NURBS models.
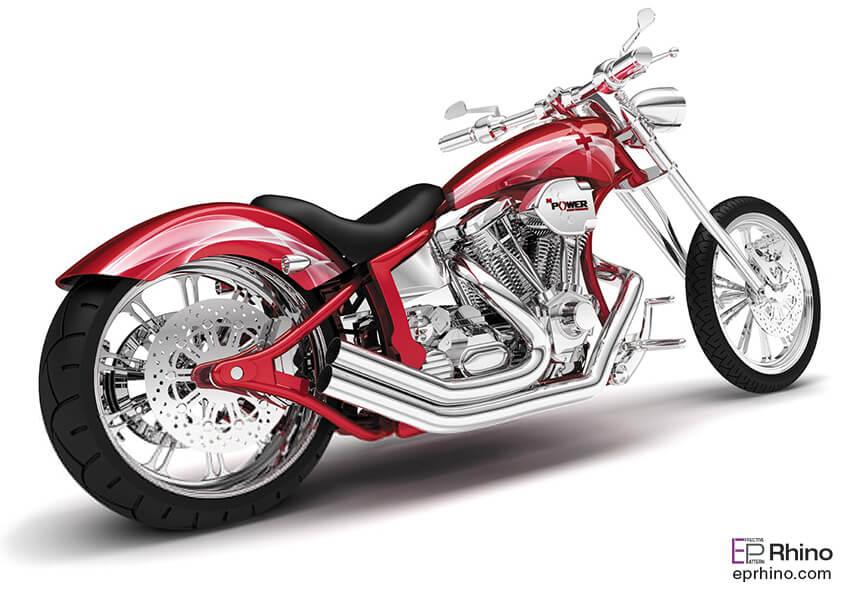

NURBS provides a compact and unified approach to modeling 3D surfaces. Users can create both simple and complex surfaces using splines. Let’s delve deeper into some graphical terms that are common across modeling software. In the past, when drawing curves by hand, flexible metal or wooden strips (or any flexible material like bendable rulers) were used to create curves. As you know, at least three points are needed to draw a curve, as infinitely many curves can pass through two points. So, given at least three points and a spline (the flexible strip), the curve was drawn by bending the metal over the points. This tool later gave its name to these types of curves. In other words, splines today represent a type of curve. Mathematically, splines represent polynomial functions in a coordinate system. These functions can be simple like ax+b or more complex polynomial functions like ax^2 + bx + c. By selecting two points, a sequence of line segments is created between these points, resulting in a curved line. However, in computer graphics, a curved line does not exist as an independent data element. The curvature of the line, the smoothness of the curve, and many other parameters can only be defined visually. These parameters are determined based on the chosen curve function. In computer graphics, a curved line is composed of multiple line segments. Therefore, the more line segments, the smoother the line and the softer the curve. As you can see, the smoothness of a spline depends on the number of line segments it consists of. In all 3D graphics software, the number of these line segments is defined parametrically. This means that you can increase or decrease the number of these line segments at any time based on your needs. As a result, a model created using splines can have a more compact or lighter structure in different parts of the modeling process.
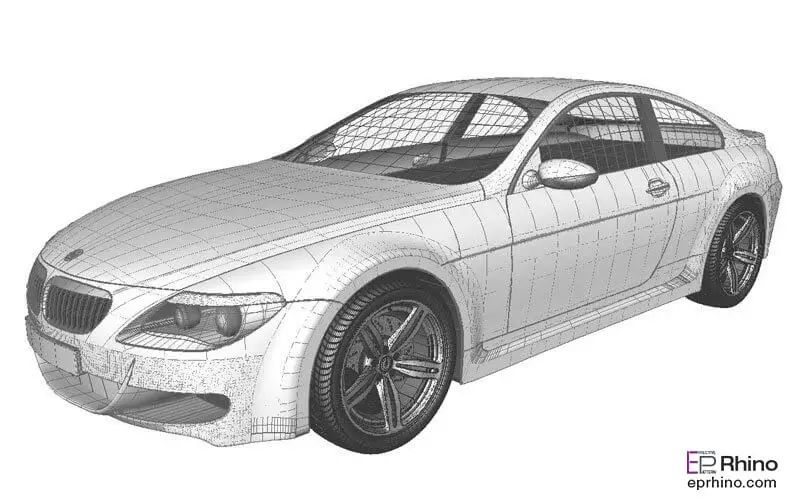

As we know, to create a plane or surface, we need at least two axes. If our surface is flat, we can draw two lines to define the plane in the scene. Now imagine using curves instead of lines to create a surface. In other words, create a surface using several splines that are not flat but have bumps and depressions corresponding to its curves. A surface created from splines is called a surface. Surfaces are formed by multiple splines.
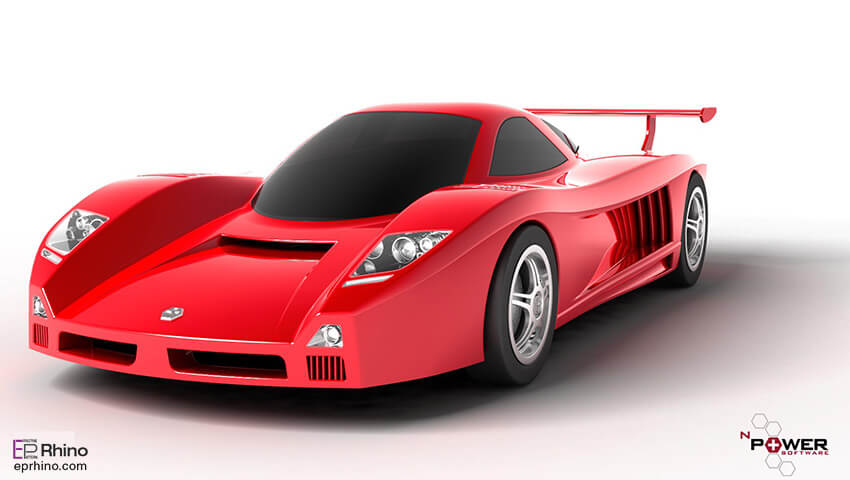

Let’s return to NURBS. As mentioned, the term is derived from Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline. B-Spline or Basis Spline refers to simple polynomial curves. The term “Non-Uniform” refers to parametric curves. These parameters indicate that a non-uniform curve consists of several points or knots that form a Bezier curve. Bezier curves are parametric curves that can parametrically define the number of points or knots of the curve and can be scaled infinitely. Therefore, a surface created by these curves is called a Bezier surface. As a result, this type of surface and curve can easily add new knots to define new curves and surfaces. Rational also refers to a mathematical definition that indicates that surfaces with this capability can be created as free-form curves, and these curves consist of a specific number of corners or knots, such as circles, ellipses, etc., which have a fixed number of points.

Let’s explain NURBS in simpler terms. NURBS is a method where parametric surfaces are created using freeform curves. As a result, surfaces created using NURBS are created parametrically, and you can change the properties of the surface at any stage. But why are NURBS surfaces important? These surfaces are easy to create and easy to edit and control. You can combine multiple NURBS surfaces to create a new surface. NURBS surfaces are smooth and have a reasonable computational load compared to similar polygon surfaces. These surfaces are controlled by points or knots, making them very easy and enjoyable for users to edit. One of the most important reasons for using NURBS modeling is the speed of production. Editing these models using control points is also very simple and fast. Due to their simplicity and controllability, NURBS modeling has become an integral part of 3D modeling software.

The second reason for using NURBS surfaces is their high quality and lower surface count. This means that by creating a model with a NURBS surface, we achieve very high quality in modeling, while the volume of the created model in terms of the number of created surfaces is much lower compared to other modeling methods such as polygon modeling. As a result, their processing speed is much higher, and since a large model is produced from a very small number of surfaces, editing that model is much easier and faster. It also puts less load on the system, making it much easier and smoother to create very complex scenes with a large number of models compared to other modeling methods. And finally, having fewer surfaces in the model will result in fewer modeling errors. Due to the structure of NURBS, these models require much less memory (RAM) than other modeling methods. Therefore, when it comes to creating highly detailed models, you can rely on the NURBS method. NURBS-generated surfaces can be easily divided into smaller surfaces without creating any gaps or seams. These surfaces connect to other surfaces like a zipper, creating a new unified surface.
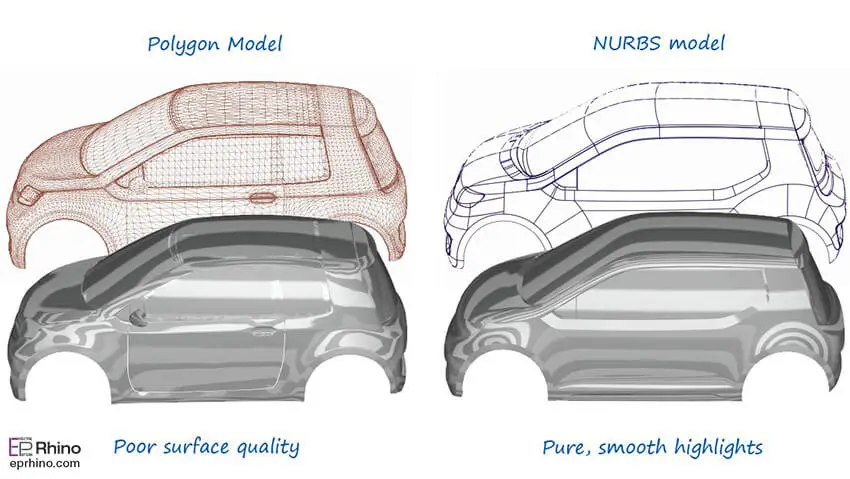
For organic modeling, it is highly recommended to use the NURBS method. In this case, the very high quality and suitable smoothness of the surfaces will make the work much easier for users. However, NURBS modeling requires sufficient skill, and if you are not familiar with this method, you will get very confused and frustrated in the middle of the modeling process. Creating a model in this method requires a predefined plan and method. You need to have a good vision of this method to be able to easily create your model, otherwise, you will encounter significant problems in model creation. Knowing which curves to use and where to connect them requires experience and skill. But if you master this method, you can easily create very complex models in the shortest time and with the highest quality. However, there are also some limitations and problems with the NURBS modeling method. First, creating complex models with diverse surfaces requires combining a large number of NURBS surfaces, which can be somewhat difficult and in some cases impossible. Unified surfaces are easy to model, but surfaces with sharp and dry edges, produced from different and multi-layered pieces, and overall not smooth, are difficult to produce with NURBS.
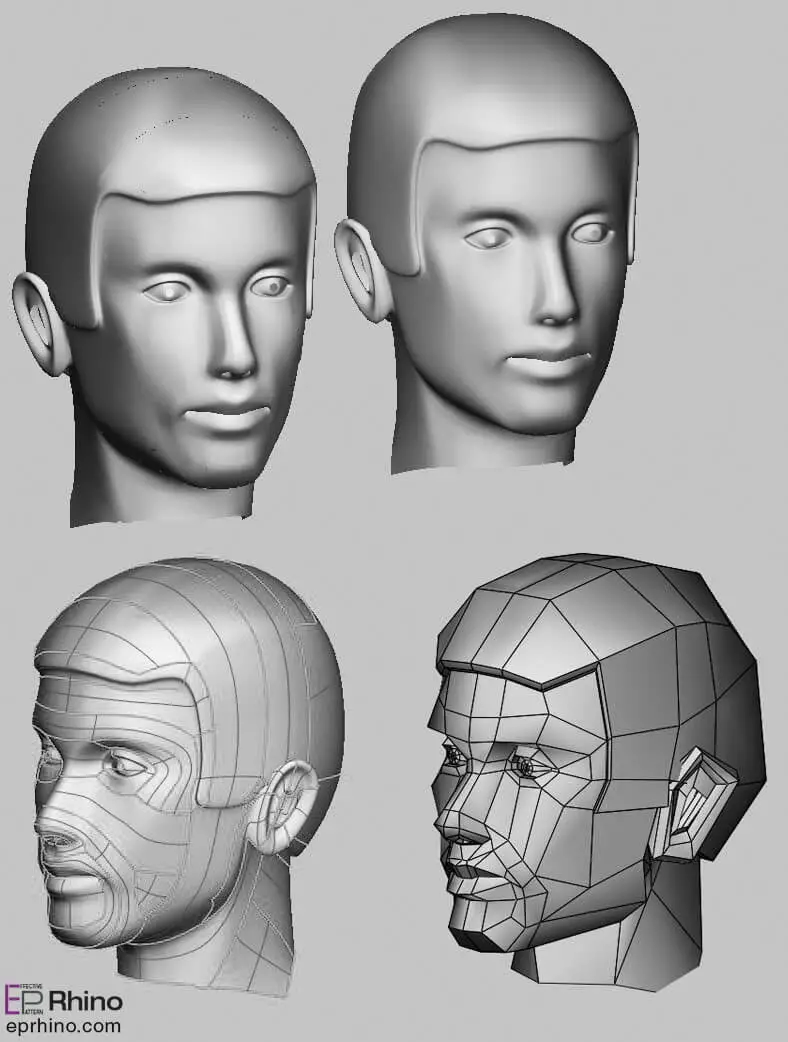
One of the main problems, especially for those who do not know where to connect the surfaces, is that when creating animations, animating the model from the seams of the surfaces is very difficult and painful. That’s why I say that this method requires good practice and experience so that you can accurately determine the location of the seams during the modeling process. In many cases, such as modeling cars, aircraft, organic models, etc., using the NURBS method is considered a principle, and using this method for the mentioned cases is very logical and fast.

Furthermore, sculpting models produced by NURBS is much lighter and faster than polygon models, and advanced techniques are available for this method. Another weakness of this modeling method is that in many rendering engines, when rendering these models, NURBS are converted to polygons, which can be very time-consuming in some cases and consume a lot of memory. Since many rendering engines use the same algorithm for lighting, there have been cases where, if NURBS are not converted to polygons, it will not be possible to light the model, and all the surfaces of these models created using the NURBS method will be dark and black and will not be able to receive light rays. It is rare to find a rendering engine that can render NURBS surfaces without converting them to polygons. For this reason, professional users convert all models to polygons using scripts and plugins before rendering the scene. In this case, they can make significant changes in memory consumption and rendering speed.
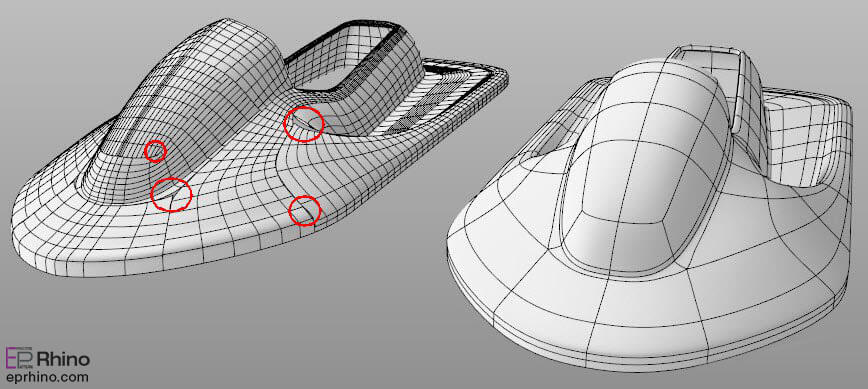
In most 3D software, there are functions that allow users to determine the density of the model when converting it to polygons during rendering. For example, you can convert a NURBS model to a polygon model with a thousand faces or convert the same model to a model with one million faces. Obviously, the choice of conversion density has a significant impact on memory consumption, rendering speed, and most importantly, render quality.




